# 1.垂直居中和水平居中方法总结
# 水平居中
- 水平居中:分为块级元素居中和行元素居中
# 一、行级元素居中(内联元素)
行级元素元素居中最简单。
行内元素就是内联元素。例如<span>、<a>、<label>、<em>、<img>等。。
直接构建一个具有 ”text-align:center“样式的块级容器,那么里面包含的行内元素就会都居中了。
# 二、块级元素居中
块级元素有:div , p , form, ul, li , ol, dl, form, address, fieldset, hr, menu, table
大家都知道块级元素是可以设置 height 和 width 的,那么这就又分为定宽与不定宽。
# 1. 定宽:margin:0 auto
- 定宽其实很好解决。直接 margin:0 auto 就可以实现容器居中,再加上 text-align:center 才可以让文本居中。
<p
style="
border-style:solid;
text-align:center;
margin:0 auto;
width:500px"
>
我是定宽块级元素,我要居中
</p>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 2. 不定宽(较常用):
不定宽其实是用的最多的,如这种导航栏:
 要居中的话有三种方法,其中一种是利用 table 标签的特性,适用性不是很好就不介绍了。
要居中的话有三种方法,其中一种是利用 table 标签的特性,适用性不是很好就不介绍了。
# 1)设置子元素为 display: inline-block/inline;给父元素设置 text-align: center;
即将其转换成行内块级/行内元素,给父元素设置 text-align: center;
- 效果:(将子元素转换成行内元素,内容的高度撑起了子元素的高度,设置高度无用)
这里其实和行级元素的处理方式是一样的
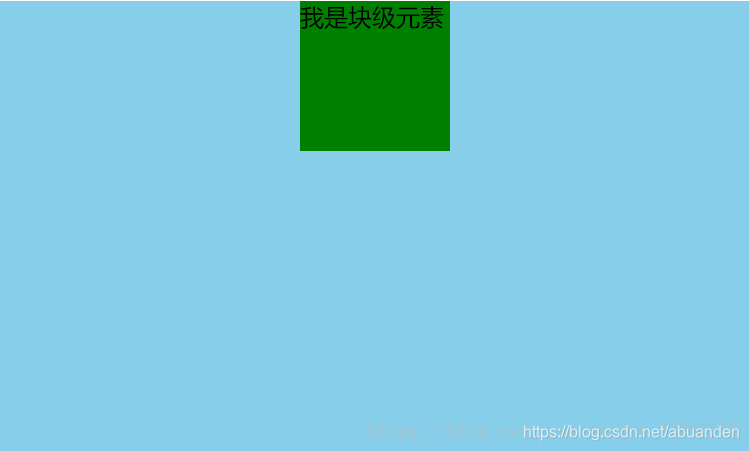
# 2) 使用定位属性
首先设置父元素为相对定位,再设置子元素为绝对定位,利用 css3 新增属性 transform: translateX(-50%);
<style>
#father {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: skyblue;
position: relative;
}
#son {
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
transform: translateX(-50%); /*看这里*/
}
</style>
<div id="father">
<div id="son">我是块级元素</div>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
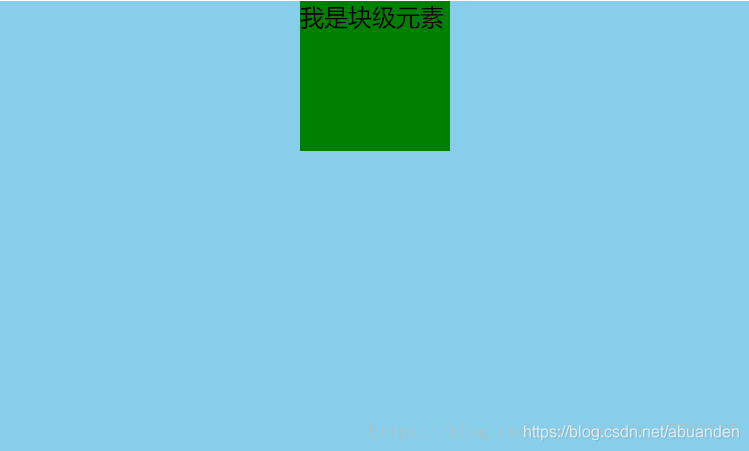
# 3. 推荐的方法:使用 flexbox 布局实现(宽度定不定都可以)
- 使用 flexbox 布局,只需要给待处理的块状元素的父元素添加属性 display: flex; justify-content: center;
<style>
#father {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: skyblue;
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
#son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
}
</style>
<div id="father">
<div id="son">我是块级元素</div>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
@TOC
# 垂直居中
# 一、单行的行内元素
# 设置单行行内元素的"行高等于盒子的高"
只需要设置单行行内元素的"行高等于盒子的高"即可;
<style>
#father {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: skyblue;
}
#son {
background-color: green;
height: 300px;
}
</style>
<div id="father">
<span id="son">我是单行的行内元素</span>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16

# 二~、多行的行内元素(很常用)(多复习)
# 使用给父元素设置 display:table-cell;和 vertical-align: middle;属即可;
<style>
#father {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: skyblue;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
#son {
background-color: green;
}
</style>
<div id="father">
<span id="son"
>我是多行的行内元素我是多行的行内元素我是多行的行内元素我是多行的行内元素我是多行的行内元素我是多行的行内元素我是多行的行内元素我是多行的行内元素</span
>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19

# 三、块级元素
# 方案一:使用定位(高度定不定都可以)
- 类似于水平居中 首先设置父元素为相对定位,再设置子元素为绝对定位,设置子元素的 top: 50%,即让子元素的左上角垂直居中;设置 transform: translateY(-50%);(
<style>
#father {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: skyblue;
position: relative;
}
#son {
width: 100px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
transform: translateY(-50%);
}
</style>
<div id="father">
<div id="son">我是块级元素</div>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20

# 方案二:使用 flexbox 布局实现(高度定不定都可以)
- 类似水平居中
<style>
#father {
width: 500px;
height: 300px;
background-color: skyblue;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
#son {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: green;
}
</style>
<div id="father">
<div id="son">我是块级元素</div>
</div>
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19

# 总结
- 设置水平垂直居中。最好用的方法有两种:
# 使用定位属性
设置父元素为相对定位,给子元素设置绝对定位。 left: 50%; top: 50%; transform: translateX(-50%) translateY(-50%);
# 使用 flex 布局实现
设置父元素为 flex 定位,justify-content: center; align-items: center;